If your document includes multiple natural languages (for example, both English and Spanish), you need to properly identify the language for each passage of text. When you do this, text-to-speech (TTS) tools will read each language using the correct pronunciation and accent. Otherwise, TTS tools may improperly read aloud Spanish-language text with an English accent, for example.
Additionally, when you properly identify the natural language of text, Microsoft Word will change the language it uses to check for spelling and grammar errors. This way, Word won’t flag your Spanish words as being misspelled.
Note that you do not need to do this for proper names, technical terms, or foreign words that have become commonplace in English (such as faux pas).
Follow these steps to properly identify the natural language of text:
- Select the relevant text.
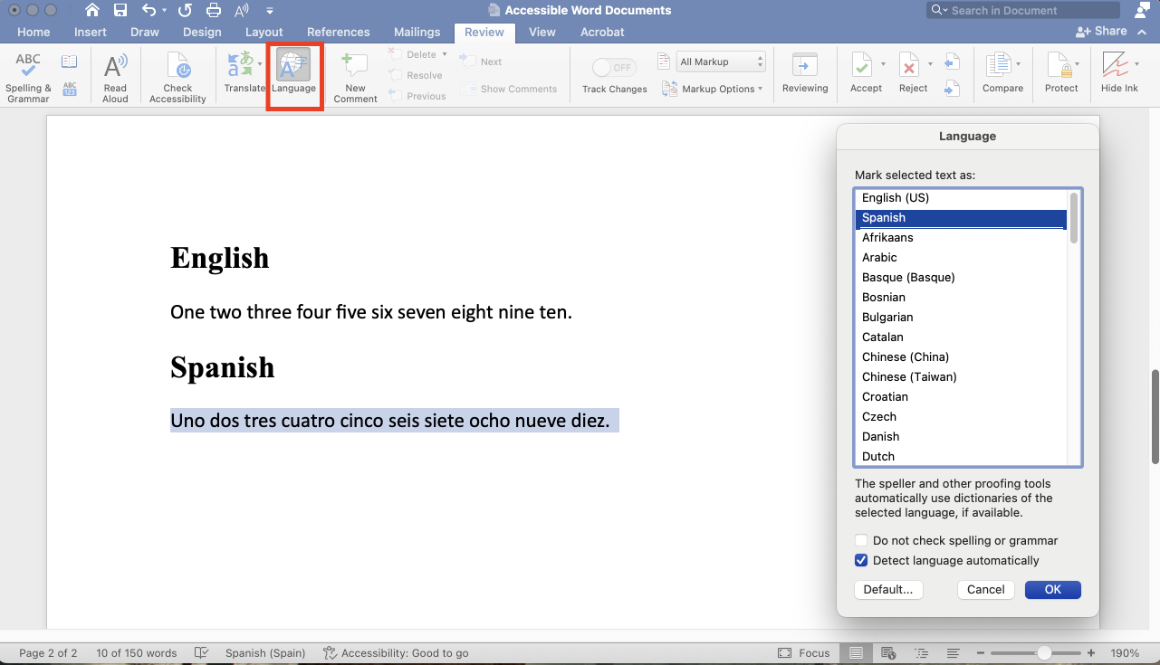
- Select the “Review” tab.
- Select “Language.”
- Choose the appropriate language and then select “OK.”
You can check your work using the Read Aloud feature under the Review tab. It will read aloud your document using text-to-speech (TTS). You should notice the pronunciation shift appropriately between languages, and you may notice the voice changing as well. Note that in order for this to work properly, you may need to first install additional languages in your system settings.